27th August 2021, 4pm – 5pm SGT

SPOT the hidden DANGER of latent TB
Active TB vs Latent TB
Of the global population, approximately 2 billion people is estimated to be infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis1. There are two types of tuberculosis (TB) conditions: active tuberculosis (TB) disease and latent TB infection (LTBI). If untreated, approximately 5%–10% of persons with LTBI may progress to active TB disease, passing the infection to others2 According to the WHO End TB Strategy, systematically providing TB preventive treatment to those at highest risk of developing active TB will prevent the development of disease and reduce the risk of transmission in the population; this is a critical step to End TB.
Latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) is a state of persistent immune response to stimulation by M. tuberculosis antigens without evidence of clinically manifested active TB3. The immune system cannot eliminate TB bacteria completely instead it is contained in the granuloma. They may develop disease in the future when the immune system weakens, making the person ill and at risk of spreading the infection.
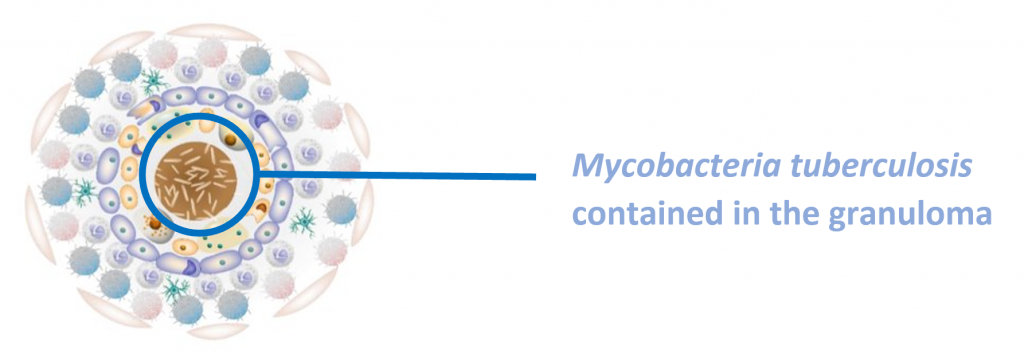
The WHO’s annual report4 on the status of global efforts to End TB notes that, at the present trajectory, most WHO regions and individual countries will fall significantly short of the End TB milestones. Hence, global TB prevention efforts along with targeted testing and treatment of latent TB infection builds a strong core TB infrastructure to realizing TB elimination. For an infection that kills 1.3 million a year, there’s routine screening or a gold standard test for LTBI5 – Either a tuberculin skin test (TST) or interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) is used. A diagnosis of LTBI first requires that active TB disease be excluded by medical evaluation.
IGRAs are whole-blood tests that measure the individual’s immune reactivity to tuberculosis. Leukocytes from most individual who have been infected with M. tuberculosis will release interferon-gamma (IFN-g) when mixed with antigens derived from M. tuberculosis. To conduct the test, fresh blood samples are extracted and mixed with antigens and controls. Two IGRAs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are6:
- QuantiFERON® – TB Gold In-Tube test (QFT–GIT);
- SPOT® TB test (T–SPOT.TB)
The antigens, testing methods, and interpretation criteria for IGRAs differ as below:
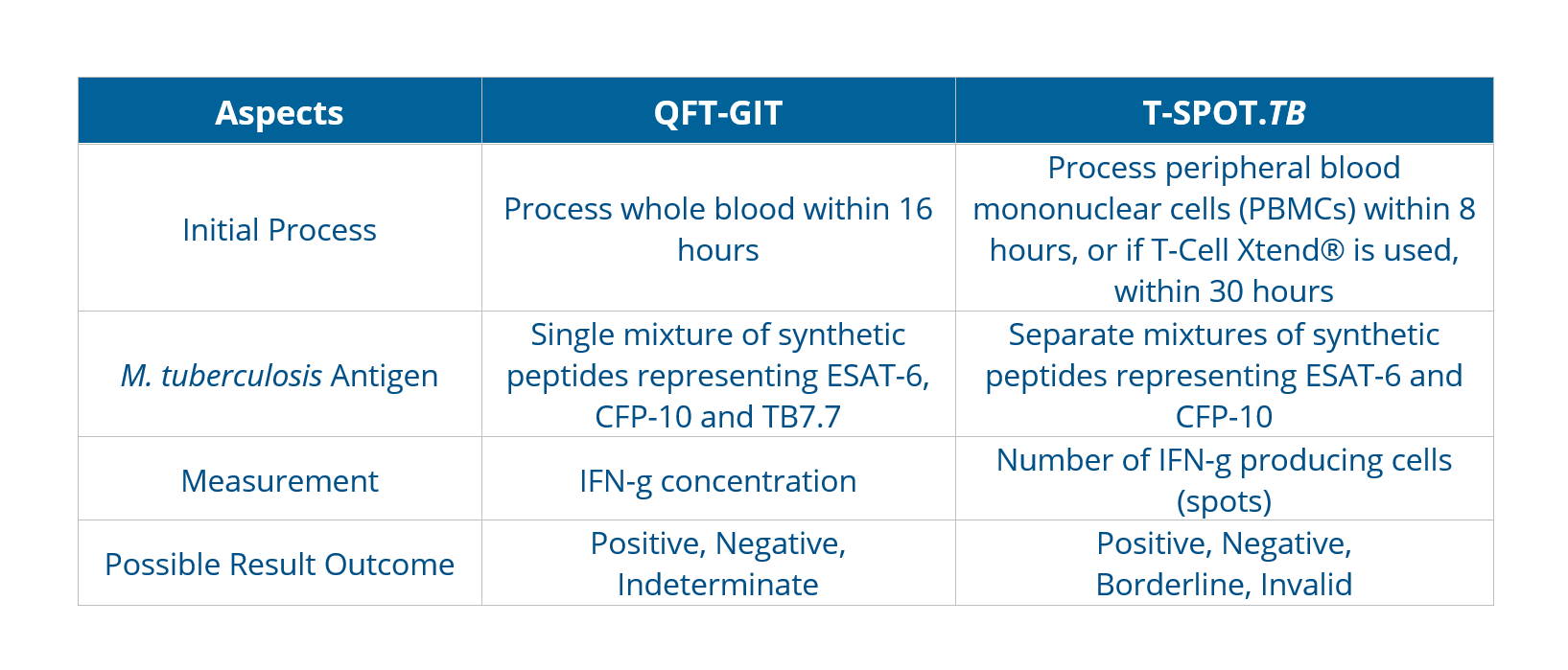
The incremental cost-effectiveness of IGRAs and TSTs appears to be influenced mainly by their accuracy. Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccination plays a decisive role in reducing the specificity of TST, leading the choice towards adopting IGRA-only strategies for better diagnostic accuracy.As with TSTs, IGRAs should be used as an aid in diagnosing latent infection with M. tuberculosis. A positive test result suggests that M. tuberculosis infection is likely; negative result suggests that infection is unlikely. An indeterminate result or borderline test result (T-Spot only) indicates an uncertain likelihood of M. tuberculosis infection6.
NOT all IGRAs are the same.
The T-SPOT.TB test is the only globally regulated IGRA that is normalised for both cell number and culture conditions in each patient specimen. The cell enumeration technology in the proprietary T-SPOT.TB test removes serum factors that could adversely affect the test result, making it the most sensitive and most specific test for TB infection7, supported by clinical data obtained even in challenging patient populations.
Learn more about the T-SPOT.TB Test here.
References:
- Houben RM, Dodd PJ. The global burden of latent tuberculosis infection: a re-estimation using mathematical modelling. PLoS Med 2016;13:e1002152.
- Sutherland I. Recent studies in the epidemiology of tuberculosis, based on the risk of being infected with tubercle bacilli. Adv Tuberc Res 1976;19:1–63.
- Latent tuberculosis infection: updated and consolidated guidelines for programmatic management. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
- WHO End TB Strategy. World Health Organization. WHO End TB Strategy. Published September 8, 2015. Assessed January 9, 2020.
- WHO End TB Strategy. Latent tuberculosis infection Updated and consolidated guidelines for programmatic management. Published 2017, Assessed November 30, 2021 via https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/260233/9789241550239-eng.pdf
- Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, Interferon-Gamma Release Assays (IGRAs) – Blood Tests for TB Infection Fact Sheets. Published May 4, 2016. Assessed November 30, 2021 via https://www.cdc.gov/tb/publications/factsheets/testing/igra.htm
- Oxford Immunotec. T-SPOT.TB Package Insert PI-TB-IVD-UK V3. Abingdon, UK. February 2019